Black screen instead of desktop in RDP session
What is RDP Remote Access and How to Solve Common Problems?
Remote desktop access (RDP) is one of the most popular tools for remotely managing computers and servers. The technology allows you to connect to another device over the network and work on it as if you were sitting at its keyboard. However, using RDP is not always without complications. In this article, we will analyze what remote access via RDP is, what problems users most often encounter, and also offer possible solutions.
Remote desktop basics: how RDP works
Remote desktop is a protocol developed by Microsoft that allows you to manage Windows operating systems over a network. RDP creates a secure communication channel between devices, providing access to a remote computer and allowing you to work with files, run programs, and perform administrative tasks.
The protocol supports various security settings and data encryption, which makes it convenient for use in a corporate environment. For example, administrators can remotely configure servers or provide technical support to employees. But despite its many advantages, there are various technical difficulties that can arise when working with RDP.
Common problems with remote connections via RDP
1. Inability to establish a connection to a remote computer
One of the most common situations is a connection error. This is usually due to the fact that the remote device is not available on the network or the ports are configured incorrectly. It can also be due to incorrectly specified credentials or lack of connection permissions.
2. Slow connection and poor performance
Delays in the RDP session can be caused by a poor Internet connection or insufficient resources on the remote computer. If the remote server has too many active tasks or its parameters are insufficient to work with several users at the same time, this can lead to significant delays in response.
3. Problems with graphics and screen display
Some users experience incorrect screen display, especially when using RDP over low-speed connections or on devices with low resolutions. Graphic artifacts, color distortions, or loss of image quality can all be caused by a mismatch between session parameters and network or device capabilities.
4. Limited access to local resources
A common situation is when users cannot access local devices, such as printers or disks, via RDP. This is usually due to incorrect session settings or security restrictions on the remote computer.
5. Sessions disconnecting after a short time
Connection interruptions during RDP sessions can occur due to security policy settings, session timeouts, or network problems. Some systems automatically terminate inactive sessions to save resources, which can create inconvenience for users.
How to solve problems with remote access via RDP?
1. Checking network settings
If the RDP session does not start, the first thing to do is to make sure that the remote computer is turned on, connected to the network, and that the necessary ports for remote access are configured on it. By default, RDP uses port 3389, and if it is blocked by a firewall, the connection will fail.
2. Optimizing performance
To troubleshoot performance issues, you should check your internet connection speed and reduce the graphics settings in the RDP client. For example, you can disable the transfer of the desktop background, window shadows, and other graphic elements to reduce the load on the network.
3. Configuring the screen and graphics
To improve the display quality, you can adjust the screen resolution and refresh rate in the RDP settings. If the problems are related to poor internet quality, you can try connecting via VPN, which can improve stability and data transfer speed.
4. Configuring access to local resources
To use local devices via RDP, you need to make sure that the transfer of printers, disks, and other devices is enabled in the client settings. It is also important to check that the necessary drivers are installed on the remote computer and access to these resources is allowed.
5. Increase session time
If your RDP session is regularly interrupted, you can check the timeout settings in the system security policy or in the remote access settings. Increasing the idle time before disconnecting can help avoid frequent connection breaks.
Remote access via RDP is a powerful and convenient tool for managing computers and servers, but its use can be accompanied by various problems. Understanding common errors and knowing how to solve them will help ensure stable RDP operation and improve the remote work experience.
Solving the problem
During an RDP session, press CTRL+ALT+END followed by Cancel. Often this way you can return to the desktop of the RDP session. If it doesn’t help, launch the Task Manager and the File Explorer process (File -> Run new task -> explorer.exe -> Ok);
 1. Check that caching is disabled in the RDP client (mstsc.exe) settings (turn off Persistent bitmap caching on the Experience tab) and that the screen resolution is used.
1. Check that caching is disabled in the RDP client (mstsc.exe) settings (turn off Persistent bitmap caching on the Experience tab) and that the screen resolution is used.
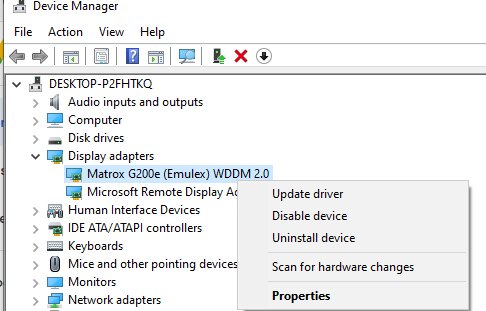
 It is supported by the remote host. Check that your PC has the latest video driver. You can install drivers manually or set them to update automatically.
It is supported by the remote host. Check that your PC has the latest video driver. You can install drivers manually or set them to update automatically.
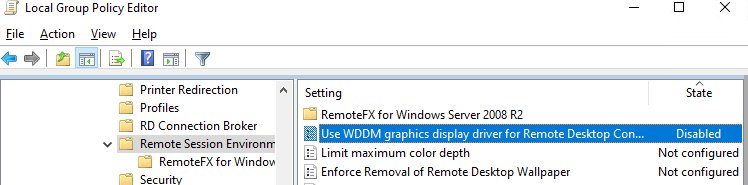
 2. For Windows 10 you need to insert using XDDM instead of WDDM. Open the group policy editor gpedit.msc and in the section Computer Configuration -> Administrative Templates -> Windows Components -> Remote Desktop Services -> Remote Desktop Session Host -> Remote Session Environment set the value of the parameter Use WDDM graphics display driver for Remote Desktop Connections = Disabled . We update group policies on the RDP server.
2. For Windows 10 you need to insert using XDDM instead of WDDM. Open the group policy editor gpedit.msc and in the section Computer Configuration -> Administrative Templates -> Windows Components -> Remote Desktop Services -> Remote Desktop Session Host -> Remote Session Environment set the value of the parameter Use WDDM graphics display driver for Remote Desktop Connections = Disabled . We update group policies on the RDP server.
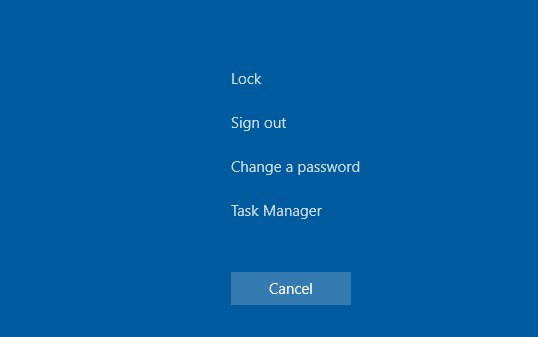
 3. In Windows Server 2016, with timeouts set for RDS sessions, users sometimes receive complaints that after connecting to a disconnected session, it did not activate correctly and they saw a black screen. The only thing that will help here is to end the RDP session by the user himself (CTRL+ALT+End -> Sign out),
, or forced termination of the session by the administrator (similar to the article The required operation cannot be completed when logging in via RDP). Or configure more aggressive settings for disabling disconnected sessions;
We disable the use of the UDP 3389 protocol for transmitting RDP traffic in addition to the standard RDP port TCP 3389 through the Turn off UDP on client parameter on the client (Computer Configuration -> Policies -> Administrative Templates -> Windows Components -> Remote Desktop Services -> Remote Desktop Connection Client) or through the registry: reg add “HKLM\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows NT\Terminal Services\Client” /v “fClientDisableUDP” /t REG_DWORD /d 1 /f .
To disable the UDP protocol for RDP traffic on the server side, configure the GPO parameter. Remote Desktop Session Host -> Connections -> Select RDP transport protocols = Use only TCP.
3. In Windows Server 2016, with timeouts set for RDS sessions, users sometimes receive complaints that after connecting to a disconnected session, it did not activate correctly and they saw a black screen. The only thing that will help here is to end the RDP session by the user himself (CTRL+ALT+End -> Sign out),
, or forced termination of the session by the administrator (similar to the article The required operation cannot be completed when logging in via RDP). Or configure more aggressive settings for disabling disconnected sessions;
We disable the use of the UDP 3389 protocol for transmitting RDP traffic in addition to the standard RDP port TCP 3389 through the Turn off UDP on client parameter on the client (Computer Configuration -> Policies -> Administrative Templates -> Windows Components -> Remote Desktop Services -> Remote Desktop Connection Client) or through the registry: reg add “HKLM\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows NT\Terminal Services\Client” /v “fClientDisableUDP” /t REG_DWORD /d 1 /f .
To disable the UDP protocol for RDP traffic on the server side, configure the GPO parameter. Remote Desktop Session Host -> Connections -> Select RDP transport protocols = Use only TCP.
 4. Among the more exotic recommendations from Microsoft, which do not always help, but can correct the source of the problem:
- We check the RDP server, client and all network equipment between them. They must be configured to the same MTU.
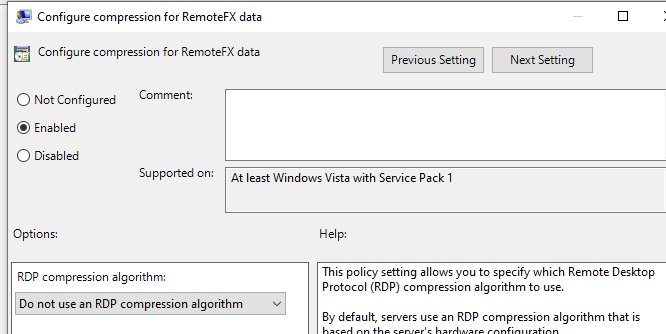
- We turn off the option to compress the data that is sent in the RDP session through the local GPO editor – Configure compression for RemoteFX data = Do not use an RDP compression algorithm (Computer Configuration -> Administrative Templates -> Windows Components -> Remote Desktop Services -> Remote Desktop Session Host).
- If the black screen issue in RDP occurs on Windows Server 2019 and Windows 10 1809+. Open Event Viewer and check the Application and Service Logs -> Microsoft -> Windows -> RemoteDesktopService-RdpCoreTS event log.
Check if there are errors like ‘ Failed GetConnectionProperty’ in CUMRDPConnection::QueryProperty at 2884 err=[0x80004001] ‘, ‘ Connection doesn’t support logon error redirector’ in CUMRDPConnection::GetLogonerrorRedirector at 4199 err=[0x80004001].
- If there is, disable the use of the URCP (Universal Rate Control Protocol), which is used to transfer some data between the RDP client and the server over UDP (MS-RDPEUDP2): reg add “HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Terminal Server Client” /v “UseURCP ” /t REG_DWORD /d 0 /f or so New-ItemProperty 'HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Terminal Server Client' -Name UseURCP -PropertyType DWord -Value 0
4. Among the more exotic recommendations from Microsoft, which do not always help, but can correct the source of the problem:
- We check the RDP server, client and all network equipment between them. They must be configured to the same MTU.
- We turn off the option to compress the data that is sent in the RDP session through the local GPO editor – Configure compression for RemoteFX data = Do not use an RDP compression algorithm (Computer Configuration -> Administrative Templates -> Windows Components -> Remote Desktop Services -> Remote Desktop Session Host).
- If the black screen issue in RDP occurs on Windows Server 2019 and Windows 10 1809+. Open Event Viewer and check the Application and Service Logs -> Microsoft -> Windows -> RemoteDesktopService-RdpCoreTS event log.
Check if there are errors like ‘ Failed GetConnectionProperty’ in CUMRDPConnection::QueryProperty at 2884 err=[0x80004001] ‘, ‘ Connection doesn’t support logon error redirector’ in CUMRDPConnection::GetLogonerrorRedirector at 4199 err=[0x80004001].
- If there is, disable the use of the URCP (Universal Rate Control Protocol), which is used to transfer some data between the RDP client and the server over UDP (MS-RDPEUDP2): reg add “HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Terminal Server Client” /v “UseURCP ” /t REG_DWORD /d 0 /f or so New-ItemProperty 'HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Terminal Server Client' -Name UseURCP -PropertyType DWord -Value 0